
Introduction
For many people in India, farming is their primary source of income, and they make their living from agriculture, so farming and agriculture are important to the nation’s economy.
India has a long farming history and ranks among the world’s leading producers of a wide range of crops, including pulses, wheat, and rice. The country’s diverse land types, climates and rainfall patterns allow for a wide variety of farming practices, including organic farming in India.
In addition to providing people with food, agriculture also supplies raw materials for industries. In addition to boosting the rural economy, it also generates jobs in villages. Traditional farming practices are gradually changing slowly with modern techniques.
However, in India today, both traditional and modern techniques are used. We can better understand how food is produced and how farmers in India manage their land and resources to support the nation by being aware of the various farming practices practised here.
Major Types of Farming in India
A. Subsistence Farming
Growing food primarily for their own family’s consumption is known as subsistence farming. Farmers use traditional methods and basic tools for this type of farming.
The farms are small and neither chemicals nor machinery are used very often.
Wheat pulses and rice are common crops. The majority of this kind of farming occurs in rural regions of states like West Bengal, Odisha and Bihar, where people rely on farming for their daily food.
B. Commercial Farming
The purpose of commercial farming is to generate revenue by selling crops in the market. Modern equipment, chemicals and tools are used to achieve a good crop.
Cash crops such as tea, cotton and sugarcane are grown by farmers. More land and water are required for this kind of farming. It is typical in states with larger farms and better facilities for large-scale farming, such as Punjab, Haryana, and Maharashtra.
C. Organic Farming
Using natural methods and without the use of synthetic fertilizers or chemicals, organic farming is one of the best Types of farming in India.
It enhances soil health and uses environmentally friendly methods. Organic farming in India requires more work and produces less, but the food is safer and healthier.
Additionally, the cost of production is higher. Because of clean and natural farming practices, states like Sikkim, Kerala, and Uttarakhand are among the top states doing organic farming.
D. Plantation Farming
Plantation farming is a method in which a single crop is cultivated over a sizable land area. Both a lot of work and effective management are required for this type of farming. Spices, tea, coffee and rubber are important crops grown with this type of farming.
Typically this farming is used by tropical or hilly regions like Assam, Kerala and Karnataka, and these states are renowned for their plantation farming because of their best soil and climate.
E. Mixed Farming
Mixed farming is when farmers who grow both crops and livestock on the same property, which is one of the Types of farming in India.
It supports farmers’ income in many ways. Cows, goats and poultry are also raised alongside crops like rice and wheat.
This type of farming is typical in states like Punjab, Haryana and Uttar Pradesh, where farming and animal care are highly developed.
F Dryland Farming
Dryland farming is done in regions with dry soil and little rainfall. Farmers face many challenges because water is not easily available in these regions. Oilseeds, pulses, millets and other crops with lower water requirements are cultivated in this type of farming.
Special techniques are used to preserve crops and conserve water. This type of farming is commonly seen in regions with dry climates like Rajasthan, Maharashtra, and Andhra Pradesh.
G. Irrigation Farming
Particularly in regions with less rainfall, irrigation farming uses water from wells, rivers or canals to grow crops. For improved crop growth and more harvests, it is important for Indian agriculture.
Drip irrigation, tube wells, and canal irrigation are typical techniques used in this type of farming. Tamil Nadu and Punjab are two states that heavily rely on irrigation farming. It increases food production by helping farmers in growing crops all year round.
H. Shifting Cultivation (Jhum Farming)
Shifting cultivation is a traditional farming method of tribal people. They clear the portion of forest land and then plant crops there for a few years and then move to a new area.
It is prevalent in Odisha and Northeast India. Although it supports tribal life, it harms the environment through deforestation and soil loss.
I Hydroponics & Modern Farming Techniques
A contemporary method of soilless farming is hydroponics. Water that contains nutrients is used to grow plants and is one of the Types of farming in India.
It is a component of urban farming and conserves water and space. Cities and places with poor soil can benefit from these techniques.
The use of drones, greenhouse farming and vertical farming is also increasing and they have great potential to produce nutritious food in the future using fewer resources and less land.
Government Initiatives Supporting Different Farming Types
To help farmers the Indian government has launched several programs. Small farmers receive financial help directly from PM-KISAN to meet their needs. Farmers can better understand their soil condition and the appropriate fertilizers to use by using the Soil Health Card.
By providing guidance and assistance to farmers who cultivate crops without the use of chemicals, the Paramparagat Krishi Vikas Yojana (PKVY) promotes organic farming in India. To make it easier for farmers to obtain water for their fields the government also provides irrigation subsidies.
In addition to lowering expenses, subsidies for organic farming in India promote natural farming practices. These actions support various farming practices like organic and sustainable farming while also lowering farming expenses and improving crop quality.
Challenges Faced by Indian Farmers
Crop cultivation in India is challenging due to climate change and monsoons. Rainfall can be either too much or too little at times because of this the crops suffer. The high cost of seeds, fertilizer and equipment is another issue that farmers face.
Many people take loans and end up in debt. Market access is another significant problem. A lot of the time, farmers are unable to sell their crops at major markets. They are subject to price swings, even if they do the prices fluctuate excessively.
Farmers find it difficult to make a consistent living because of these issues. For small and marginal farmers, all of these difficulties make farming dangerous and stressful. Organic farming in India is emerging as a potential solution, promoting lower input costs and healthier soil, while also offering premium market opportunities.
Future of Farming in India
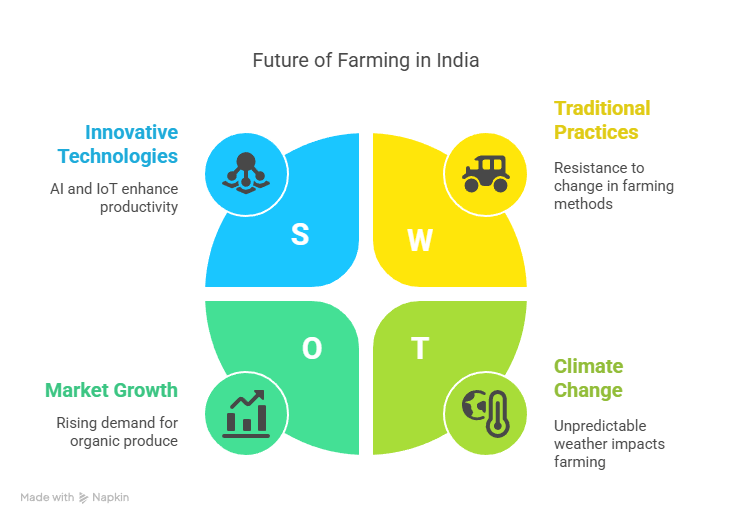
India’s farming industry appears to have a bright future because of the new technology. The best time to water, fertilize or harvest crops is determined by farmers with the help of technologies like artificial intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (IoT). Data-driven precision farming produces more food with less waste.
Climate-smart techniques are also being taught to farmers to safeguard crops against weather variations. Additionally, there is a rising demand for organic food and innovative farming practices like hydroponics, which grows crops in water rather than soil.
These innovative concepts have the potential to increase farmers’ incomes, reduce their resource consumption and save the environment for coming generations.
Conclusion
India offers a wide range of farming practices, including modern organic, traditional and cutting-edge techniques like hydroponics. Each variety contributes differently to the nation’s food needs. However, farmers today confront significant obstacles like market issues, high costs and climate change.
At Mytan Farms, we believe that modern farming equipment and technology are essential for agricultural progress. We are committed to combining innovation with climate-friendly and sustainable practices. Modern farming equipment and technology are both important for the progress of farming in India. We must simultaneously stick to climate-friendly and sustainable practices.
By taking these actions, farmers will be able to produce more food, increase their incomes and protect the environment. The future of farming in India will depend on how well farmers use or combine innovative concepts with sustainable and intelligent farming practices.
FAQs on Types of Farming in India
1. What is the most common type of farming in India?
In India, subsistence farming is the most popular and common type of farming. In this way, farmers primarily cultivate crops for their consumption. They use basic tools and rely on rainfall to stay hydrated. In this kind of farming, wheat, rice, and pulses are frequently grown.
2. Which states in India are known for commercial farming?
Gujarat, Maharashtra, Punjab and Haryana are renowned for their commercial farming. Farmers cultivate crops for the market under this type. They make use of fertilizers, irrigation and contemporary tools. Common commercial crops include cotton, sugarcane and groundnut.
3. What are the benefits of organic farming?
Both the environment and human health benefit from organic farming. It makes use of organic fertilizers like cow dung and compost instead of dangerous chemicals. It generates nutritious food, maintains clean water and enhances soil quality. It also aids in the protection of birds and insects.
4. How does plantation farming differ from other types?
Large tracts of land are used for plantation farming, which involves growing a single crop for profit. They grow crops like bananas, tea, coffee and rubber. A large workforce, funds and reliable transportation are required. Other farming practices frequently use small areas to grow a variety of crops.
5. What is the future of farming in India?
India’s farming industry is heading toward sustainability and technology. The use of smart farming techniques like drip irrigation improved seeds and machinery. Climate-friendly and organic farming will also grow, boosting farmers’ incomes and preserving the environment.




